Introduction to Cat6 Standards
● Overview of Cat6 Cabling
Cat6 cables, also known as Category 6 cables, are a type of Ethernet cabling used for network installations. Introduced to support higher data transfer rates, Cat6 cables are widely used in both residential and commercial environments for their superior performance compared to their predecessors, like Cat5 and Cat5e. Cat6 cables can support data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps over short distances (up to 55 meters) and 1 Gbps over longer distances (up to 100 meters). This makes them an essential component in modern network infrastructures.
● Importance of Adhering to Standards in Ethernet Cabling
Adhering to industry standards is crucial in Ethernet cabling to ensure compatibility, performance, and reliability. These standards, often set by organizations like the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and International Organization for Standardization (ISO), dictate the physical and electrical properties of the cables. Compliance ensures that different brands and types of cables can work together seamlessly within the same network. For Cat6 cables, the standard requires specific parameters to be met, including the use of 23AWG conductors.
Understanding American Wire Gauge (AWG)
● Explanation of AWG
The American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a standardized system for wire diameters used primarily in North America. The gauge number inversely relates to the wire diameter—meaning a lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire. For instance, a 23AWG wire is thicker than a 24AWG wire. The thickness of the wire impacts its electrical properties, such as resistance and the ability to carry current.
● Significance of Wire Gauge in Electrical and Data Transmission
The thickness of a wire, represented by its AWG, significantly influences its performance in electrical and data transmission. Thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) have lower resistance, which allows for better signal integrity and less attenuation (signal loss). For data cables like Cat6, a thicker wire means better performance over longer distances, which is crucial for maintaining high-speed data transfer rates.
23AWG vs. 24AWG: Key Differences
● Differences in Conductor Diameter
The primary difference between 23AWG and 24AWG wires lies in their diameter. A 23AWG wire has a larger diameter than a 24AWG wire. This difference in size affects several key properties of the wire, including its resistance and the amount of signal attenuation. In simpler terms, a 23AWG wire can carry signals more efficiently over longer distances compared to a 24AWG wire.
● Impact on Cable Performance and Durability
The larger diameter of 23AWG wires results in lower electrical resistance, which means signals can travel further and faster with less degradation. This directly translates to improved performance for network cables, especially in high-performance scenarios like high-speed internet and data centers. Additionally, thicker wires are generally more durable and less susceptible to damage during installation, making them a more reliable choice for long-term deployments.
Why Cat6 Requires 23AWG
● Compliance with EIA/TIA Standards
Cat6 cables are designed to meet specific performance criteria set by industry standards like EIA/TIA-568. These standards stipulate that Cat6 cables must use 23AWG conductors to achieve the desired electrical properties, including minimal signal loss and high data transmission speeds. Using 23AWG conductors ensures that the cables can support Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet applications effectively.
● Specific Performance Metrics Met by 23AWG
The use of 23AWG in Cat6 cables allows them to meet various performance metrics, such as attenuation, crosstalk, and return loss. These metrics are crucial for maintaining high-speed data transmission and overall network performance. For instance, 23AWG cables have lower attenuation, meaning less signal degradation over distance, and better crosstalk performance, ensuring minimal interference between twisted pairs within the cable.
Impact of 23AWG on Signal Transmission
● Reduction in Signal Attenuation
One of the primary benefits of using 23AWG conductors in Cat6 cables is the significant reduction in signal attenuation. Attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength as it travels through the cable. Thicker wires (lower AWG) have less resistance, which translates to less signal loss. This is particularly important for maintaining high-speed data transmission over longer distances, making 23AWG an optimal choice for Cat6 cables.
● Better Performance Over Longer Distances
The reduced attenuation provided by 23AWG conductors means that Cat6 cables can maintain higher data transfer rates over longer distances compared to cables with thinner conductors. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from short-distance connections in home networks to longer runs in commercial and industrial settings. The ability to perform reliably over longer distances without significant loss of signal quality is a key advantage of using 23AWG in Cat6 cables.
Technical Parameters of 23AWG in Cat6
● Twisting Rate and Its Influence
The twisting rate of the wire pairs within a Cat6 cable also plays a crucial role in its performance. The twisting helps to cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduce crosstalk between pairs. For 23AWG Cat6 cables, the increased wire diameter allows for optimal twisting rates that enhance performance. This precise twisting, combined with the thicker 23AWG conductors, ensures that Cat6 cables meet the stringent requirements for high-speed data transmission.
● Insulation and Jacketing Considerations
In addition to the conductor size, the insulation and jacketing of Cat6 cables are critical for performance. The insulation material must support the electrical properties of the 23AWG conductors, providing minimal signal loss and resistance. The outer jacket protects the cables from physical damage and environmental factors. For 23AWG Cat6 cables, manufacturers typically use high-quality materials to ensure both the internal and external components contribute to the overall performance and durability of the cable.
Comparing Cat6 and Cat6A Cabling
● Differences in Gauge and Construction
While both Cat6 and Cat6A cables are designed for high-speed Ethernet, they differ in several key aspects. Cat6 cables typically use 23AWG conductors, while Cat6A cables can use either 22AWG or 23AWG conductors. Cat6A cables have additional shielding and more stringent construction to support even higher data rates and longer distances than Cat6. The enhanced construction of Cat6A cables makes them suitable for 10 Gigabit Ethernet over the full 100-meter distance, unlike Cat6 which is limited to 55 meters for the same speed.
● When to Use Each Type of Cable
The choice between Cat6 and Cat6A depends on the specific requirements of the network. For most residential and small office networks, Cat6 cables with 23AWG conductors provide ample performance for Gigabit Ethernet and limited 10 Gigabit Ethernet applications. However, for larger networks, data centers, and applications requiring 10 Gigabit Ethernet over longer distances, Cat6A cables are the preferred choice due to their enhanced performance and reduced interference.
23AWG in Shielded vs. Unshielded Cat6 Cables
● Role of Shielding in Cable Performance
Shielding in network cables helps to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). Shielded Cat6 cables (F/UTP or S/FTP) include an additional layer of shielding around the individual pairs or the entire cable, providing extra protection in environments with high EMI. The use of 23AWG conductors in shielded Cat6 cables further enhances their performance, particularly in terms of signal integrity and interference resistance.
● Applications for Shielded vs. Unshielded Cables
Shielded Cat6 cables are often used in industrial settings, data centers, and other environments with significant electrical interference. Unshielded Cat6 cables (UTP), on the other hand, are suitable for most residential and office installations where EMI is not a significant concern. Both shielded and unshielded cables benefit from the use of 23AWG conductors, as they provide the necessary performance and durability for high-speed data transmission.
Practical Applications of 23AWG Cat6 Cable
● Typical Environments and Use Cases
23AWG Cat6 cables are versatile and can be used in a wide range of environments, from home networks to large commercial installations. They are ideal for structured cabling systems in office buildings, providing reliable connections for computers, IP phones, and other networked devices. Additionally, they are used in educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and retail settings where high-speed, reliable network connectivity is essential.
● Benefits in Specific Scenarios Like Higher Data Rates and Longer Runs
In scenarios where higher data rates and longer cable runs are required, 23AWG Cat6 cables provide significant benefits. Their thicker conductors reduce signal attenuation, ensuring that data transfer rates remain high even over extended distances. This makes them suitable for applications such as connecting remote workstations, establishing backbone connections between network hubs, and supporting high-bandwidth devices like video conferencing systems and high-definition security cameras.
Conclusion: Optimal Cabling Practices
● Summary of Why 23AWG is Essential for Cat6
The use of 23AWG conductors in Cat6 cables is essential for meeting industry standards and ensuring optimal performance. The thicker wires provide lower resistance, reduced signal attenuation, and better overall performance, making them ideal for high-speed data transmission over longer distances. Compliance with EIA/TIA standards further ensures that Cat6 cables with 23AWG conductors deliver reliable, consistent performance in various network environments.
● Recommendations for Choosing and Installing Cat6 Cables
When selecting Cat6 cables, it is crucial to choose products that adhere to industry standards and use 23AWG conductors. Working with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, such as those specializing in wholesale cat6 23awg, can ensure that you receive high-quality cables that meet your specific needs. Proper installation practices, including careful handling and adherence to recommended distances and termination techniques, are also essential for maximizing the performance and longevity of your network cabling.
About Aston Cable
Aston Cable factory is located in Hangzhou Linan City, just two hours away from Shanghai Pudong Airport or Xiaoshan Airport by car. With over 20 years of experience in manufacturing communication cables, Aston Cable boasts advanced manufacturing machines and testing equipment. The factory covers 10,000 square meters and has a daily production capacity of around 500km. Aston Cable's main products include Coaxial Cable, Composited Cable, Lan Cable, alarm cable, and other security cables. The company is committed to improving customer satisfaction by providing high-quality products and professional solutions.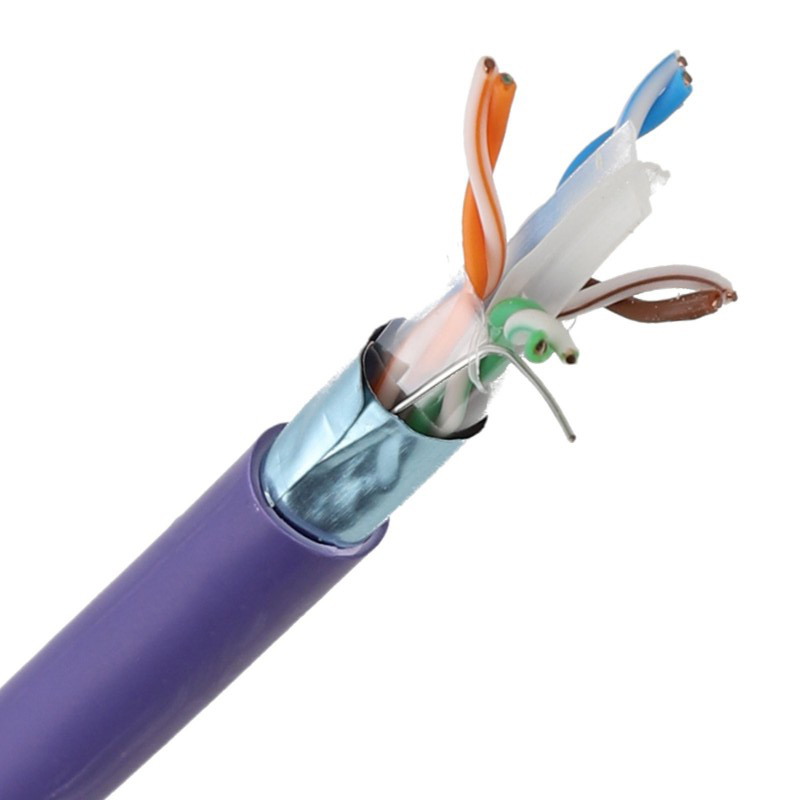
Post time: 2024-11-07 16:34:06